Exercise
1. Answer the following questions.
(a) What is a ‘cell’?
Ans. The cell is the fundamental structural and functional unit of living organisms. Cells form the basis of the structure and function of all living organisms. It is only with the help of cells that living organisms carry out all their different life processes. Cells are extremely minute in size.
(b) Name the different organelles in a cell?
Ans. Depending upon whether it is a plant or animal cell the cells may contain the following cell organelles:
Cell membrane, cell wall, vacuole, plastids, endoplasmic reticulum, chloroplast, golgi bodies, ribosomes, mitochondria, nucleus, lysosomes, centrosome and inclusion bodies.
(c) What are micro-organisms?
Ans. The organisms which cannot be seen with our eyes but can only be observed under a microscope are called micro-organisms.
(d) Which are the different types of micro-organisms?
Ans. According to shape, and lifeprocesses, micro-organisms are classified as algae, fungi, protozoa, bacteria and viruses.
2. Fill in the blanks with the proper word.
(a) The organelle called the chloroplast is present in plant cells only.
(b) Garbage is converted into compost by micro-organisms.
(c) In the cell, photosynthesis is carried out with the help of chloroplast.
(d) An electron microscope is necessary for the study of cells .
3. What is difference between us?
(a) Plant cell and animal cell.
| Plant Cell | Animal Cell |
| 1. Plant cells have a cell wall, as well as a cell membrane. | 1. Animal cells simply have a cell membrane, but no cell wall. |
| 2. A plant cell contains a large, singular vacuole | 2. Animal cells have many, smaller vacuoles. |
| 3. A plant cell is larger as compared to an animal cell | 3. An animal cell is smaller than a plant cell. |
| 4. Animal cells have lysosomes | 4. Plant cells rarely contain lysosomes |
| 5. Plastids are present in plant cell. | 5. Plastids are absent in animal cell. |
(b) Prokaryotic cell and eukaryotic cell.
| Prokaryotic cell | Eukaryotic cell |
| 1. Usually unicellular | 1. Usually multicellular |
| 2. Nucleus is absent. | 2. Nucleus is present. |
| 3. Endoplasmic reticulum is absent. | 3. Endoplasmic reticulum is present |
| 4. Mitochondria is present. | 4. Mitochondria is absent. |
| 5. Ribosomes are smaller. | 5. Ribosomes are absent |
4. Sketch and describe in your own words, the plant cell and animal cell.
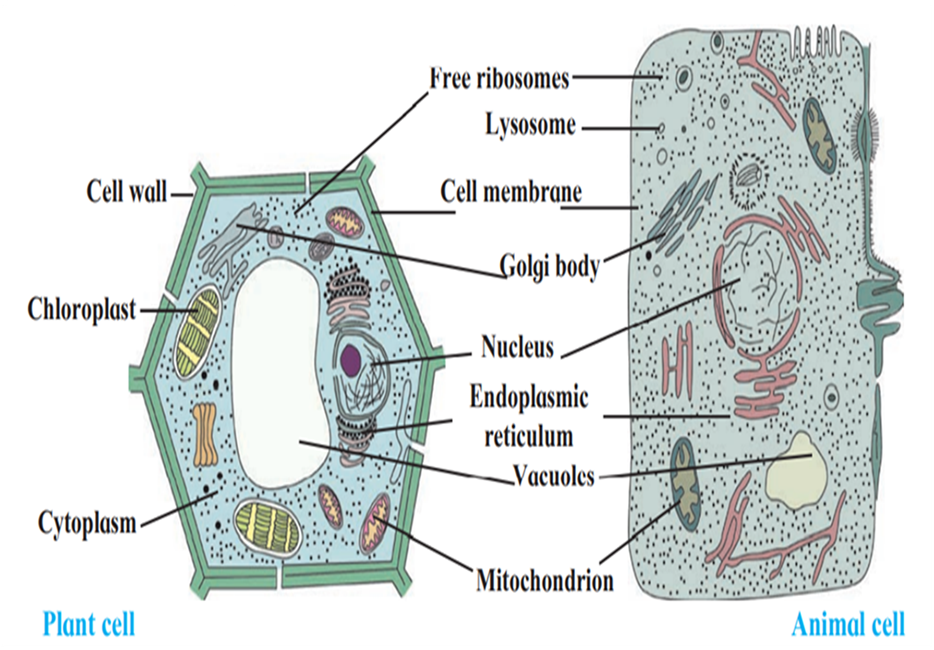
The cell has four main parts – the cell wall, cell membrane, cytoplasm and cell organelles.
(a) Cell wall : The cell wall is the outermost covering of a cell. It is present only in plant cells.
(b) Plasma membrane : The plasma membrane, also called the cell membrane, is a kind of thin covering. It is extremely delicate and flexible. It is the outermost covering of animal cells.
(c) Cytoplasm : The liquid part in the cell, present around the nucleus is called cytoplasm. It occupies the space between the plasma membrane and nucleus. Cell organelles are scattered in the cytoplasm.
(d) Cell organelles : These mainly include the nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi bodies, lysosomes, mitochondria, vacuoles, plastids, etc. Plant cells contain chloroplasts.
The nucleus is the most important organelle of the cell. There is a porous double membrane around it. The nucleus controls all functions of the cell. The endoplasmic reticulum is a sprawling net-like organelle. Its function is to make necessary changes in the proteins produced by ribosomes and send them to the Golgi bodies. Golgi bodies are made up of several flat sacs. Their function is the proper distribution of proteins. Mitochondria and plastids are organelles with double outer coverings. As mitochondria produce energy, they are called the powerhouses of the cell. The chloroplasts in plant cells carry out the function of photosysthesis. Vacuoles help to throw out waste products of the cell. Vacuoles in animal cells are small whereas there is only one large vacuole in a plant cell.
5. Explain the uses and the harmful effects of micro-organisms.
Ans. Uses of micro-organisms:
(i) Micro – organisms help in the fermentation of idli & dosa batter, conversion of milk into curds, making yeast for preparing bread, etc.
(ii) Microbes decompose the dead and decaying remains of plants and animals.
(iii) Microbes decompose the garbage to obtain food material. As a result, garbage is soon converted into manure of the best quality and our surroundings are kept clean.
(iv) For proper sewage disposal, too, microbes are released into the sewage so as to help in the quick decomposition of the organic compounds in it.
(v) Some micro-organisms present in the soil and those in the root nodules of leguminous plants convert atmospheric nitrogen into its compounds. These nitrogenous compounds help to increase soil fertility and thereby the protein content of the pulses grown in that soil.
(vi) A vaccine is produced in a laboratory with the help of microbes, that gives immunity against a particular disease.
(vii) Microbes are also used in processes like tanning of skin, production of ropes and strings from agave.
(viii) Some microbes use oil for their growth. Such microbes are used to clear a layer of oil floating on the surface of an ocean or lake formed due to a leak or a spill i.e. to clear an oil slick.
Harmful effects of micro-organisms:
(i) As micro-organisms use foodstuffs for their own nutrition, some microbes release toxic materials, into the food. Such toxins spoil the food. Eating such spoiled food can cause loose motions and vomiting.
(ii) Pathogens may be present in water bodies contaminated with sewage and dirt from the surroundings, in food left uncovered in unhygienic conditions with houseflies sitting on it, etc. If such contaminated food or water is consumed, we may fall ill with diseases of the alimentary canal, like amoebiasis, typhoid, cholera, hepatitis, gastro, etc.
(iii) Pathogens are released in the air when a person having an infection of the respiratory tract sneezes or coughs. A healthy person may get infected with such pathogens on breathing in the same air and contract diseases like common cold, cough, diphtheria, pneumonia, tuberculosis, etc.
(iv) Mosquitoes reproduce in places like heaps of garbage, drains, stagnant water, etc. Microbes that cause diseases like malaria, dengue, elephantiasis, yellow fever, chikungunya, Zika fever, etc. gain entry into the human body through the bite of a female mosquito.
6. Give reasons.
(a) Diseases spread on a large scale during periods of heavy rainfall and floods.
Ans. During heavy rainfall and floods, water may get accumulated for some time which may lead to breeding of mosquitoes and other micro-organisms, thus spreading diseases.
(b) There is a possibility of food poisoning if we eat stale food.
Ans. Fungus grows quickly on moist and stale food. Some microbes release toxic materials (enterotoxins), into the food. Such toxins spoil the food. Eating such spoiled food can cause loose motions and vomiting.
(c) Soil is turned over during tilling.
Ans. Micro-organisms present in the soil help in decomposing of dead and decaying remains of plants and animals thus increasing the fertility of soil. By turning the soil during tiling the micro-organisms get spread out even thus speeding the process of decomposition and fertility of the soil.
(d) Fungus grows quickly in moist or humid conditions.
Ans. Moist and humid conditions are favourable for the growth of fungus. Therefore, they grow quickly in moist and humid conditions.
(e) A refrigerator is used in almost every home.
Ans. The optimum temperature for the growth of microorganisms,150 C to 350 C. The temperature inside a household refrigerator is maintained at 40 C. Microbes cannot grow at this temperature and there food is prevented from spoilage. Therefore, a refrigerator is used in almost every home.
(f) Bread ‘rises’ during baking.
Ans. Yeast, a kind of fungus, is added to the bread dough. The yeast cells start the process of fermentation, which is a chemical process of conversion of one type of carbon compound into another type of carbon compound. Heat is generated and carbon dioxide and some other gases are released. These gases cause an increase in volume and the bread dough is seen to ‘rise’.
(g) Fodder is soaked in water before offering to cattle.
Ans. Soaking the fodder helps in hydrating it as well as starting the process of fermentation. Thus increasing the nutritive value of the fooder.
7. When will you use a simple microscope and when, a compound microscope? Explain in detail how you will use them.
Ans. A microscope is an instrument that magnifies an object. Microscopes are used in laboratories to observe cell that cannot be seen through our naked eye.
A simple microscope uses a lens or set of lenses to enlarge an object through angular magnification alone, giving the viewer an erect enlarged virtual image.
It is used by students in the school laboratory to observe insect parts or parts of flowers, etc.
A compound microscope uses a lens close to the object being viewed to collect light which focuses a real image of the object inside the microscope. That image is then magnified by a second lens or group of lenses (called the eyepiece) that gives the viewer an enlarged inverted virtual image of the object. The use of a compound objective/eyepiece combination allows for much higher magnification. These are used by research scientists and students.
Project : Visit a bakery in your area, collect information about the process of manufacture of their products and make one of them at home.
Extra Textual Questions:
What is the name of the minute components of which the body of a living organism is made ?
Ans. The minute components of which the body of a living organism is made are cells.
Is the number of these smallest units the same in the bodies of all living organisms ?
Ans. The number of these smallest units the same in the bodies of all living organisms is not the same. Unicellular organisms have a single cell where as multicellular organisms will have many cells.
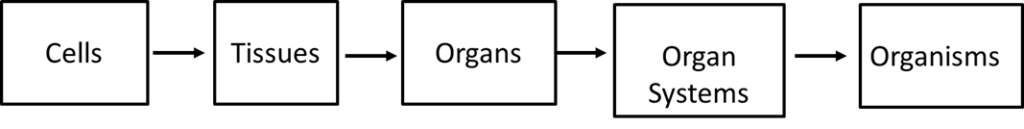
Complete the flow chart:

Which are the common components of plant and animal cells ? Which are the different ones ?
Ans. The common components of plant cell and animal cell are: nucleus, cell membrane, free ribosomes, golgi body, endoplasmic reticulum, vacuoles and mitochondria.
Components present only plant cell are: cell wall, chloroplast and cytoplasm.
Components present only in animal cell are: lysosomes.
Use your brain power !
Where do the life processes of unicellular organisms take place ?
Ans. Unicellular organisms are made of a single cell, all life processes take place in the single cell.
How do the cells acquire definite shapes ?
Animal cells acquire definite shape with the help of plasma membrane or cell membrane. Whereas plant cell acquire their definite shape with the help of cell wall.
How are cells protected ?
Ans. Cells are protected by the cell wall or cell membrane.
What are the needs of cells ?
Cells are the basic structures of all living organisms.
Cells provide structure to the body, take in nutrients from food and carry out important functions.
Groups of cells together form tissues, groups of tissues form organs, such as the heart, brain, etc.
Our cells contain a number of components called organelles.
These organelles carry out various functions and perform the life processes of the body.
Why should dry and wet waste be collected separately ?
Ans. Dry waste can be recycled and wet waste can be converted into manure by treating it with micro-organisms.
Why is yoghurt mixed in the batter or dough for making rava-idli, bhature, naan ?
Ans. When yoghurt is mixed with the batter or dough, the microbes present in it start multiplying and start the process of fermentation. Heat is generated in this process and carbon dioxide and some other gases are released. These gases cause an increase in volume, in the batter or dough in which yoghurt was added.
How do preparations like yoghurt, idli, dosa become easy to digest?
Ans. Microbes present in yoghurt, idli, dosa grow in the batter and dough. They break down the substances producing new compounds as they grow and multiply in them. This helps the food to digest easily.
How will you know that a foodstuff is spoilt ?
Ans. A round layer of white scum or black particles may appear to have formed on the surface and the foodstuff may give out a bad odour.
What precautions will you take while purchasing food ? Why ?
Ans. We should take the following precautions while purchasing food
(a) Check the expiry date.
(b) The packaging should not be damaged or torn.
(c) The foodstuff should not have changed colour.
(d) It should not give out a bad smell.
(e) Purchase foodstuff that was stored in clean and hygienic condition.
We should take the above precautions, as otherwise the foodstuff may be infected with microbes. If such contaminated food or water is consumed, we may fall ill with diseases of the alimentary canal, like amoebiasis, typhoid, cholera, hepatitis, gastro, etc.
Why do food poisoning incidents occur during marriage or other community feasts ?
Ans. During marriage or other community feasts, food is prepared in large quantities. Often the caterers do not maintain proper temperature or hygiene which may lead to contamination of food. Consuming such contaminated food may lead to food poisoning.
What is meant by micro-organisms ?
The organisms which cannot be seen with our eyes but can only be observed under a microscope are called micro-organisms.
Categorise the following organisms into two groups, according to size – amoeba, paramoecium, euglena, snail, elephant, pigeon, worms.
| Unicellular | Multicellular |
| amoeba, paramoecium, euglena | snail, elephant, pigeon, worms |
Where do the micro-organisms grow?
Medium : Soil, water, decaying matter, etc.
Temperature : 25० – 37० .
Nutrition : specific nutrients, e.g. algae-chlorophyll, oxygen.
Atmosphere : Moist, humid, warm
Observe the roots of the pea, bean and fenugreek plants. What could be the functions of the nodules on their roots ?
Ans. Some micro-organisms present in the soil and those in the root nodules of leguminous plants convert atmospheric nitrogen into its compounds. These nitrogenous compounds help to increase soil fertility and thereby the protein content of the pulses grown in that soil.
What does your mother do to make yoghurt from milk ?
Ans. To make yoghurt from milk mother takes a few drops of yoghurt or buttermilk and mixes with lukewarm milk and keeps it at that temperature for 8-10 hours, microbes present in the drops of yoghurt quickly multiply and the milk gets converted into yoghurt.
Who discovered the process of fermentation ?
Ans. Louis Pasteur
Why are infants vaccinated according to a fixed time schedule ?
Ans. Vaccination helps our bodies immunity i.e. resistance to that disease, increases, so that the possibility of contracting that disease is greatly reduced. Therefore, infants are vaccinated according to a fixed schedule.
What is a vaccine?
A vaccine is produced in a laboratory with the help of microbes, that gives immunity against a particular disease.
What happens to the sweetmeat or bread forgotten in a lunch-box for three or four days?
Ans. A round layer of white scum or black particles may appear to have formed on the surface. on the sweetmeat or bread forgotten in a lunch-box for three or four days.
What do we do with spoilt food? Why ?
Ans. We throw the spoilt food, because the fungus that grows on spoilt food release toxic materials (enterotoxins), into the food. Eating such spoiled food can cause loose motions and vomiting.
Which diseases do microorganisms cause in plants and animals ?
Ans. (a) Diseases in plants are:
Blight
• Citrus Canker
• Rust
• Smut
• Tobacco mosaic
(b) Diseases caused in animals:
Anthrax Bacterium
Foot-and-mouth infection
What exactly happens when we have fever ?
The body temperature of a healthy human being is about 370 C If micro-organisms enter our body, our immune system starts acting and body temperature rises. This destroys the micro-organisms. The site of an injury also feels warm for the same reason.
What is the corelation between the normal body temperature of humans which is 370 C and the optimum temperature for the growth of microorganisms, 150 C to 350 C?
Ans. The body temperature of a healthy human being is about 370 C If micro-organisms enter our body, our immune system starts acting and body temperature rises. This destroys the micro-organisms.
Can you tell ? 1. What happens if clothes remain damp in the rainy season? 2. What are the black or white spots sometimes seen on gunny bags? 3. Why are leather articles like purses, wallets, belts, footwear always polished before storing away? 4. What is the powdery material found on old currency notes or old rubber or paper?
Ans. All the materials mentioned above i.e. gunny bags, cotton clothes, paper, rubber, etc. are plant products and leather is an animal product. In a humid atmosphere, fungi and some other micro-organisms grow on these articles and spoil or damage them.
 JK Academy
JK Academy