Maharashtra Board Class 9 Science Chapter 7 Energy Flow in an Ecosystem
Class 9 Science Chapter 7 Energy Flow in an Ecosystem Textbook Questions and Answers
1. Complete the following table (Carefully study the carbon, oxygen and nitrogen cycles).
| Bio-geo-chemical cycles | Biotic processes | Abiotic processes |
| 1. Carbon cycle | Photosynthesis, Respiration, Decomposition | Burning of fossil fuels, forest fires, volcanic activity. |
| 2. Oxygen cycle | Photosynthesis, Respiration, Decomposition. | Combustion, Corrosion, rusting, formation of ozone (O3 ) |
| 3. Nitrogen cycle | Biological nitrogen fixation, ammonification, nitrification, denitrification | Atmospheric nitrogen fixation, industrial nitrogen fixation. |
2. Correct and rewrite the following statements and justify your corrections.
a. Carnivores occupy the second trophic level in the food chain.
Ans. Correct Statement: Carnivores occupy the third trophic level in the food chain.
Justification: In the food chain, producers occupy the first level, the herbivores depend on producers, therefore they occupy the second tropical level. The carnivores feed on herbivores and so occupy the third tropic level.
b. The flow of nutrients in an ecosystem is considered to be a ‘one-way’ transport.
Ans. Correct Statement: The flow of nutrients in an ecosystem is cyclic.
Justification: Nutrients, necessary for the growth of organisms are continuously transferred from abiotic to biotic factors and biotic to abiotic factors within an ecosystem. This cycle operates continuously through the medium of the biosphere formed by the lithosphere, atmosphere and hydrosphere. Hence the flow of nutrients in an ecosystem is cyclic.
c. Plants in an ecosystem are called primary consumers.
Correct Statement: Plants in an ecosystem are called producers.
Justification: Green plants in the ecosystem produce their own food in the presence of sunlight, by the process of photosynthesis. Hence they are called producers. Whereas herbivores, consume plants and so they are called primary consumers.
3. Give reasons.
a. Energy flow through an ecosystem is ‘one way’.
Ans:
- The Sun is the most important source of energy in any ecosystem.
- Green plants of the ecosystem store some amount of solar energy in the form of food.
- Before reaching the decomposers, this energy is passed on from one trophic level to the next.
- Decomposers dissipate some amount of energy in the form of heat.
- However, no part of the energy ever returns to the Sun.
- Hence, energy flow through an ecosystem is ‘one way’.
b. Equilibrium is necessary in the various bio-geo-chemical cycles.
Ans:
- The cyclic flow of nutrients within an ecosystem is called bio-geo-chemical cycles.
- Nutrients, necessary for the growth of organisms are continuously transferred from abiotic to biotic factors and biotic to abiotic factors within an ecosystem.
- The link between the biotic and abiotic factors will break, if there is any imbalance in the cycles.
- Therefore, equilibrium is necessary between bio-geo-chemical cycles.
c. Flow of nutrients through an ecosystem is cyclic.
Answer:
- All organisms need nutrients for their growth.
- The plants take the nutrients from the soil and convert it into carbohydrates through the process of photosynthesis in te presence of sunlight.
- The plants are consumed by the herbivores, the herbivores are eaten by the carnivores.
- When all living things die, they are decomposed by the decomposers. The nutrients are released into the biosphere.
- Thus nutrients are continuously transferred from abiotic to biotic factors and biotic to abiotic factors within an ecosystem.
- This cycle operates continuously through the medium of the biosphere formed by the lithosphere, atmosphere and hydrosphere.
- Hence the flow of nutrients in an ecosystem is cyclic.
4. Explain the following cycles in your own words with suitable diagrams.
a. Carbon cycle.
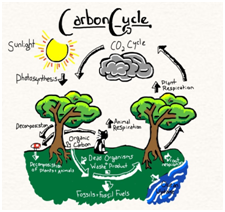
Answer:
- The circulation and recycling of carbon from the atmosphere to living organisms and after their death back to the atmosphere is called the carbon cycle.
- Abiotic carbon atoms are circulated and recycled into biotic form mainly through photosynthesis and respiration.
- Hence, the carbon cycle is one of the important bio-geochemical cycles.
- Plants convert carbon dioxide into carbohydrates by the process of photosynthesis.
- Similarly, they produce carbon compounds like proteins and fats, too.
- Herbivores feed on plants.
- Carnivores feed upon herbivores.
- In this way, biotic carbon is transported from plants to herbivores, from herbivores to carnivores and from carnivores to apex consumers.
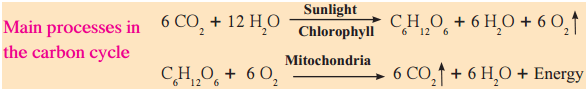
- Eventually, after death, all types of consumers, are decomposed by decomposers like bacteria and fungi and carbon dioxide is released again into the atmosphere and is used again by living organisms.
- In this way, carbon is continuously passed on from one living organism to another.
- After the death of living organisms, carbon goes to the atmosphere and is again taken up by living organisms.
b. Nitrogen cycle.
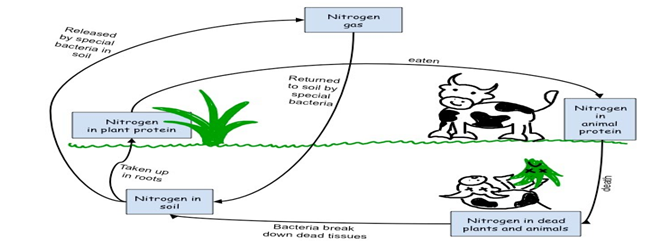
Answer:
- Nitrogen forms 78% i.e. the maximum portion of the atmosphere. It is necessary for the maintenance of the cycle of nature.
- The circulation and recycling of nitrogen gas into the form of different compounds through various biotic and abiotic processes in nature is called the nitrogen cycle.
- All organisms participate in the nitrogen cycle. It is an important component of proteins and nucleic acids.
- As compared to other elements, it is inactive and does not easily combine with other elements.
- Most organisms cannot use the free form of nitrogen.
- Important processes of nitrogen
cycle:
(a) Nitrogen fixation: Conversion of nitrogen into nitrates and nitrites through atmosphere, industrial and biological processes.
(b) Ammonification: Release of ammonia through the decomposition of dead bodies and excretory wastes of organisms.
(c) Nitrification: Conversion of ammonia into a nitrite and then nitrate.
(d) Denitrification: Conversion of nitrogen compounds into gaseous nitrogen.
c. Oxygen cycle.
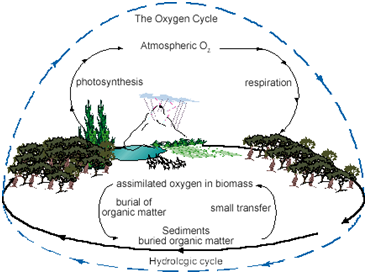
- Oxygen forms 21% of the atmosphere.
- It is also present in the hydrosphere and lithosphere.
- Circulation and recycling of oxygen within the biosphere is called the oxygen cycle.
- This cycle, includes both the biotic and abiotic components.
- Oxygen is continuously produced as well as used up in the atmosphere.
- Oxygen is highly reactive and it readily reacts with other elements and compounds.
- As oxygen is found in various forms like molecular oxygen (Oz), water (H,0), carbon dioxide (C02), inorganic compounds etc, the oxygen cycle of the biosphere is extremely complex.
- Oxygen is released in the process of photosynthesis, whereas it is used up in processes like respiration, combustion, decomposition, corrosion, rusting, etc.
5. What would you do to help maintain the equilibrium in the various bio-geochemical cycles? Explain in brief.
Answer:
- The cyclical flow of nutrients within an ecosystem is called the bio-geo-chemical cycle.
- Climatic changes and human activities seriously affect the speed, intensity and equilibrium of these cycles.
- We should make all efforts to maintain this equilibrium in nature.
- The equilibrium of oxygen and carbon dioxide gases in the atmosphere is maintained by plants. We should avoid cutting down of trees.
- We should also cut down the use of fossil fuels, and petroleum products in our vehicles. Instead we should use CNG, or electric cars.
6. Explain in detail the inter-relationship between the food chain and food web.
Answer:
- Interaction go on continuously between producers, consumers and decomposers.
- There is a definite sequence in these interactions which is called the food chain.
- Each chain consists of four, five or more links.
- An ecosystem consists of many food chains that are interconnected at various levels. Thus, a food web is formed.
- An organism may be the prey for many other organisms.
- For example, an insect feeds upon leaves of various plants but the same insect is the prey for different animals like frog, wall lizard, birds, etc.
- Many food chains connected together form an intricate web called as food web.
7. State the different types of bio-geochemical cycles and explain the importance of those cycles.
Answer:
- The cyclical flow of nutrients within an ecosystem is called the bio-geo-chemical cycle.
- There are various bio-gio-chemical cycles operating in the ecosystem. They are the oxygen, carbon, nitrogen, water, iron, calcium, phosphorous, etc.
- These cycles operate continuously through the medium of the biosphere formed by the lithosphere, atmosphere and hydrosphere.
- Nutrients and energy, necessary for the growth of the organisms are continuously transferred from abiotic to biotic factors and biotic to abiotic factors within an ecosystem.
- These cycles help in maintaining the equilibrium in an ecosystem. Thus are very important.
8. Explain the following with suitable examples.
a. What type of changes occur in the amount of energy during its transfer from plants to apex consumers?
Answer:
- Plants of the ecosystem store some of the solar energy in the form of food.
- Before reaching the decomposers, this energy is passed on from one trophic level to the next.
- At every trophic level, some amount of energy is used by the organism for its own life processes and some amount of energy is lost to the surroundings.
- Decomposers dissipate some amount of energy in the form of heat.
- However, no part of the energy ever returns to the Sun. Hence, such passage of energy is referred to as ‘one way’ transport.
b. What are the differences between flow of matter and of energy in an ecosystem? Why?
Answer:
| Flow of matter | Flow of energy |
| (i) It involves the circulation and recycling of nutrients in a cyclic manner within the biosphere. | (i) It involves the flow of energy from one trophic level to another in a unidirectional or non-cyclic manner. |
| (ii) There is no dissipation of matter at any level. | (ii) There is the dissipation of energy at every level. |
| (iii) Biosphere is the source of nutrients. | (iii) The Sun is the most important source of energy. |
 JK Academy
JK Academy