Maharashtra State Board Class 9 Science Solutions Chapter 6 Classification of Plants
Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Classification of Plants Textbook Questions and Answers
Exercise:
1. Match the proper terms from columns A and C with the description in column B.
| A | B | C |
| Thallophyta | Seeds are formed in fruits. | Fern |
| Bryophyta | No natural covering on seeds. | Cycas |
| Pteridophyta | These plants mainly grow in water. | Tamarind |
| Gymnosperms | These plants need water for reproduction. | Moss |
| Angiosperms | Tissues are present for conduction of water and food. | Algae |
Ans.
| A | B | C |
| Thallophyta | These plants mainly grow in water | Algae |
| Bryophyta | These plants need water for reproduction | Moss |
| Pteridophyta | Tissues are present for conduction of water and food | Fern |
| Gymnosperms | No natural covering on seeds | Cycas |
| Angiosperms | Seeds are formed in fruits | Tamarind |
2. Complete the sentences by filling in the blanks and explain those statements.
(angiosperms, gymnosperms, spore, Bryophyta, thallophyta, zygote)
a. ……………….. plants have soft and fiber-like body.
b. ……………….. is
called the ‘amphibian’ of the plant kingdom.
c. In pteridophytes, asexual reproduction occurs by ……………….. formation and
sexual reproduction occurs by ………………..formation.
d. Male and female flowers of ……………….. are borne on different sporophylls of
the same plant.
Answer:
a. Thallophyta plants have soft and fibre-like body.
b. Bryophyte is called the ‘amphibian’ of the plant kingdom.
c. In pteridophytes, asexual reproduction occurs by spore formation and sexual reproduction occurs by zygote formation.
d. Male and female flowers of gymnosperms are borne on different sporophylls of the same plant.
3. Answer the following questions in your own words.
a. Write the characteristics of subkingdom Phanerogams.
Ans:
- Plants which have special structures for reproduction and produce seeds are called Phanerogams.
- In these plants, after the process of reproduction, seeds are formed which contain the embryo and stored food.
- During the germination of the seed, the stored food is used for the initial growth of the embryo.
- Depending upon whether seeds are enclosed in a fruit or not phanerogams are classified into gymnosperms and angiosperms.
b. Distinguish between monocots and dicots.
Ans:
| Dicots | Monocots | |
| Seed | Two cotyledons | Single cotyledon |
| Root | Well developed, primary root (Taproot) | Fibrous roots |
| Stem | Strong, hard. e.g. Banyan tree |
Hollow,
e.g. Bamboo False, e.g. Banana Disc-like, e.g. Onion. |
| Leaf | Reticulate venation | Parallel venation |
| Flower | Flowers with 4 or 5 parts or in their multiples (tetramerous or pentamerous) | Flowers with 3 parts or in multiples of three (trimerous). |
c. Write a paragraph in your own words about the ornamental plants called ferns.
Ans.
- Ferns belong to the group of plants called Pteridophyta.
- They have well-developed roots, stem and leaves but do not bear flowers and fruits.
- They have separate tissues for the conduction of food and water.
- They reproduce with the help of spores formed along the back or posterior surface of their leaves.
- They reproduce asexually by spore formation and sexually by zygote formation.
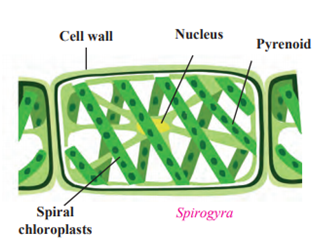
d. Sketch, label and describe the Spirogyra.
e. Write the characteristics of the plants belonging to division Bryophyta.
Ans:
- Bryophyta group of plants are called the amphibians of the plant kingdom because they grow in moist soil but need water for reproduction.
- These plants are thalloid, multicellular and autotrophic.
- They reproduce by spore-formation.
- Their plant body structure is flat, ribbon-like, long, without true roots, stem and leaves.
- Instead, they have stem-like or leaf-like parts and root-like rhizoids.
- They do not have specific tissues for the conduction of food and water.
- Examples are Moss (Funaria), Anthoceros, Riccia etc.
4. Sketch and label the figures of the following plants and explain them into brief.
Marchantia, Funaria, Fern, Spirogyra.
Ans:
Marchantia, Funaria
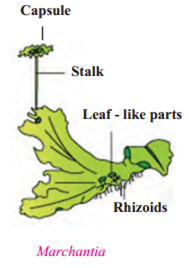

- These plants are called ‘amphibians’ of the plant kingdom because they grow mostly in soil and need water for reproduction.
- The structure of the plant body is fiat, ribbon-like long, without true roots, stem and leaves.
- Instead, they have stem-like or leaf-like parts and root-like rhizoids.
- They do not have specific tissues for the conduction of food and water.
Fern (Pteridophyta):

- Ferns belong to the group of plants called Pteridophyta.
- They have well-developed roots, stem and leaves but do not bear flowers and fruits.
- They have separate tissues for the conduction of food and water.
- They reproduce with the help of spores formed along the back or posterior surface of their leaves.
- They reproduce asexually by spore formation and sexually by zygote formation.
Spirogyra.

- Spirogyra belongs to the division thallophyta. They are called as algae.
- These plants grow mainly in water.
- This group of plants, which do not have specific parts like root-stem-leaves-flowers but are autotrophic due to the presence of chlorophyll, is called algae.
- These plants usually have a soft and fibre-like body.
5. Collect a monocot and dicot plant available in your area. Observe the plants carefully and describe them in scientific language.
6. Which criteria are used for the classification of plants? Explain with reasons.
Ans:
Criterion for classification of plants:
- The presence or absence of organs.
- The presence or absence of separate conducting tissues for conduction of water and food Do the plants bear seeds?
- If they do then, whether the seeds are enclosed in a fruit or not
- Plants are grouped depending upon the number of cotyledons in the seeds.
- Depending upon the absence or presence of flowers, fruits and seeds, plants are classified as cryptogams or phanerogams.
- Depending upon whether seeds are enclosed within a fruit or not, phanerogams are classified as gymnosperms and angiosperms.
- Angiosperms are further classified as monocots or
dicots depending upon the number of cotyledons in seeds.
Project :
a. Collect more information about plant classification from the internet, prepare a talk of about 5 to 7 minutes on that topic and present it in school during assembly.
b. Prepare an album of moncot and dicot seeds and display it in the classroom.
c. Collect photographs of 5 plants each of the Thallophyta, Bryophyta and Pteridophyta divisions and write a description of each.
Extra Textual Questions:
Can you recall?
1. How have living organisms been classified?
Ans:
(i) Organisms have been classified based on the following:
- Cell structure
- Body Organisation
- Mode of nutrition
- Reproduction
(ii) Organisms are also classified at kingdom level and groups and subgroups.
Soak
the seeds of corns, beans, groundnut, tamarind, mango, wheat, etc. in water for
8 to 10 hrs. After they are soaked, check each seed to see whether it divides
into two equal halves or not and categorize them accordingly.
Ans: Monocots: com, wheat
Dicots: beans, groundnut, tamarind and mango
 JK Academy
JK Academy